编写测试示例
此页面展示了如何为在Blueprint SDK(Sandbox)中创建的FunC合约编写测试。
测试套件为演示合约fireworks构建。Fireworks是一个通过set_first消息初始化运行的智能合约。
通过npm create ton@latest创建一个新的FunC项目后,测试文件tests/contract.spec.ts将自动生成在项目目录中,用于测试合约:
import ...
describe('Fireworks', () => {
...
expect(deployResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
...
});
});
it('should deploy', async () => {
// the check is done inside beforeEach
// blockchain and fireworks are ready to use
});
使用以下命令运行测试:
npx blueprint test
可以通过blockchain.verbosity指定附加选项和vmLogs:
blockchain.verbosity = {
...blockchain.verbosity,
blockchainLogs: true,
vmLogs: 'vm_logs_full',
debugLogs: true,
print: false,
}
直接 cell 测试
Fireworks演示了在TON区块链中发送消息的不同操作。
一旦你有足够TON金额并通过set_first消息部署它,它将使用主要和可用的发送模式组合自动执行。
Fireworks重新部署自己,结果将创建3个Fireworks实体,每个实体都有自己的ID(被保存在存储中),因此有不同的智能合约地址。
为了清晰起见,我们定义不同ID的Fireworks实例(不同的state_init)并以下列名称命名:
- 1 - Fireworks setter - 传播不同启动操作码的实体。可以扩展到四种不同的操作码。
- 2 - Fireworks launcher-1 - 启动第一个firework的Fireworks实例,意味着消息将被发送给launcher。
- 3 - Fireworks launcher-2 - 启动第二个firework的Fireworks实例,意味着消息将被发送给launcher。
展开交易细节
index - 是launchResult数组中交易的ID。
0- 对资金库(the Launcher)的外部请求,导致向fireworks发送2.5 TON的出站消息op::set_first1- 在Fireworks setter合约中使用op::set_first调用的交易,并执行了两个出站消息到Fireworks Launcher-1和Fireworks Launcher-22- 在Fireworks launcher 1中使用op::launch_first调用的交易,并执行了四个出站消息到the Launcher。3- 在Fireworks launcher 2中使用op::launch_second调用的交易,并执行了一个出站消息到the Launcher。4- 在the Launcher中来自Fireworks launcher 1的入站消息的交易。此消息以send mode = 0发送。5- 在the Launcher中来自Fireworks launcher 1的入站消息的交易。此消息以send mode = 1发送。6- 在the Launcher中来自Fireworks launcher 1的入站消息的交易。此消息以send mode = 2发送。7- 在the Launcher中来自Fireworks launcher 1的入站消息的交易。此消息以send mode = 128 + 32发送。8- 在the Launcher中来自Fireworks launcher 2的入站消息的交易。此消息以send mode = 64发送。
每个“firework” - 是交易ID:3和ID:4中出现的带有独特消息体的出站消息。
以下是每个预期成功执行的交易的测试列表。交易[ID:0]是对资金库(the Launcher)的外部请求,导致向fireworks发送2.5 TON的出站消息op::set_first。如果您将Fireworks部署到区块链,launcher会是您的钱包。
交易ID:1 成功测试
此测试检查是否通过发送2.5 TON的交易成功设置了fireworks。 这是最简单的情况,主要目的是确认交易成功属性为true。
要从launhcResult.transactions数组中过滤出特定交易,我们可以使用最方便的字段。
通过from(合约发送方地址)、to(合约目的地地址)、op(操作码值) - 我们将仅检索此组合的一个交易。
交易[ID:1]在Fireworks Setter合约中被op::set_first调用,并执行了两个出站消息到Fireworks Launcher-1和Fireworks Launcher-2。
it('first transaction[ID:1] should set fireworks successfully', async () => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(launcher.getSender(), toNano('2.5'));
expect(launchResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
from: launcher.address,
to: fireworks.address,
success: true,
op: Opcodes.set_first
})
});
交易ID:2 成功测试
此测试检查交易[ID:2]是否成功执行。
交易[ID:2]在Fireworks launcher 1中进行,用op::launch_first调用,并执行了四个出站消息到the Launcher。
it('should exist a transaction[ID:2] which launch first fireworks successfully', async () => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(launcher.getSender(), toNano('2.5'));
expect(launchResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
from: fireworks.address,
to: launched_f1.address,
success: true,
op: Opcodes.launch_first,
outMessagesCount: 4,
destroyed: true,
endStatus: "non-existing",
})
printTransactionFees(launchResult.transactions);
});
在交易要影响合约状态的情况下,可以使用destroyed、endStatus字段指定。
完整的账户状态相关字段列表:
destroyed-true- 如果现有合约因执行某个交易而被销毁。否则 -false。deploy- 自定义沙盒标志位,表明合约在此交易期间是否部署。如果合约在此交易前未初始化,而在此交易后变为已初始化,则为true。否则 -false。oldStatus- 交易执行前的账户状态。值:'uninitialized','frozen','active','non-existing'。endStatus- 交易执行后的账户状态。值:'uninitialized','frozen','active','non-existing'。
交易ID:3 成功测试
此测试检查交易[ID:3]是否成功执行。
交易[ID:3]在Fireworks launcher 1中进行,用op::launch_first调用,并执行了四个出站消息到the Launcher。
it('should exist a transaction[ID:3] which launch second fireworks successfully', async () => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(launcher.getSender(), toNano('2.5'));
expect(launchResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
from: fireworks.address,
to: launched_f2.address,
success: true,
op: Opcodes.launch_second,
outMessagesCount: 1
})
printTransactionFees(launchResult.transactions);
});
交易ID:4 成功测试
此测试检查交易[ID:4]是否成功执行。
收到来自Fireworks launcher 1的入站消息,交易[ID:4]在the Launcher(部署钱包)中进行。此消息以send mode = 0发送。
it('should exist a transaction[ID:4] with a comment send mode = 0', async() => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(
launcher.getSender(),
toNano('2.5'),
);
expect(launchResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
from: launched_f1.address,
to: launcher.address,
success: true,
body: beginCell().storeUint(0,32).storeStringTail("send mode = 0").endCell() // 0x00000000 comment opcode and encoded comment
});
})
交易ID:5 成功测试
此测试检查交易[ID:5]是否成功执行。
收到来自Fireworks launcher 1的入站消息,交易[ID:5]在the Launcher中进行。此消息以send mode = 1发送。
it('should exist a transaction[ID:5] with a comment send mode = 1', async() => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(
launcher.getSender(),
toNano('2.5'),
);
expect(launchResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
from: launched_f1.address,
to: launcher.address,
success: true,
body: beginCell().storeUint(0,32).storeStringTail("send mode = 1").endCell() // 0x00000000 comment opcode and encoded comment
});
})
交易ID:6 成功测试
此测试检查交易[ID:6]是否成功执行。
收到来自Fireworks launcher 1的入站消息,交易[ID:6]在the Launcher中进行。此消息以send mode = 2发送。
it('should exist a transaction[ID:6] with a comment send mode = 2', async() => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(
launcher.getSender(),
toNano('2.5'),
);
expect(launchResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
from: launched_f1.address,
to: launcher.address,
success: true,
body: beginCell().storeUint(0,32).storeStringTail("send mode = 2").endCell() // 0x00000000 comment opcode and encoded comment
});
})
交易ID:7 成功测试
此测试检查交易[ID:7]是否成功执行。
收到来自Fireworks launcher 1的入站消息,交易[ID:7]在the Launcher中进行。此消息以send mode = 128 + 32发送。
it('should exist a transaction[ID:7] with a comment send mode = 32 + 128', async() => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(
launcher.getSender(),
toNano('2.5'),
);
expect(launchResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
from: launched_f1.address,
to: launcher.address,
success: true,
body: beginCell().storeUint(0,32).storeStringTail("send mode = 32 + 128").endCell() // 0x00000000 comment opcode and encoded comment
});
})
交易ID:8 成功测试
此测试检查交易[ID:8]是否成功执行。
收到来自Fireworks launcher 2的入站消息,交易[ID:8]在the Launcher中进行。此消息以send mode = 64发送。
it('should exist a transaction[ID:8] with a comment send mode = 64', async() => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(
launcher.getSender(),
toNano('2.5'),
);
expect(launchResult.transactions).toHaveTransaction({
from: launched_f2.address,
to: launcher.address,
success: true,
body: beginCell().storeUint(0,32).storeStringTail("send_mode = 64").endCell() // 0x00000000 comment opcode and encoded comment
});
})
打印和阅读交易费用
在测试期间,阅读有关费用的详细信息对优化合约很有用。printTransactionFees函数以一种方便的方式打印整个交易链。"
it('should be executed and print fees', async() => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(
launcher.getSender(),
toNano('2.5'),
);
console.log(printTransactionFees(launchResult.transactions));
});
例如,在launchResult的情况下,将打印以下表格:
| (index) | op | valueIn | valueOut | totalFees | outActions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 'N/A' | 'N/A' | '2.5 TON' | '0.010605 TON' | 1 |
| 1 | '0x5720cfeb' | '2.5 TON' | '2.185812 TON' | '0.015836 TON' | 2 |
| 2 | '0x6efe144b' | '1.092906 TON' | '1.081142 TON' | '0.009098 TON' | 4 |
| 3 | '0xa2e2c2dc' | '1.092906 TON' | '1.088638 TON' | '0.003602 TON' | 1 |
| 4 | '0x0' | '0.099 TON' | '0 TON' | '0.000309 TON' | 0 |
| 5 | '0x0' | '0.1 TON' | '0 TON' | '0.000309 TON' | 0 |
| 6 | '0x0' | '0.099 TON' | '0 TON' | '0.000309 TON' | 0 |
| 7 | '0x0' | '0.783142 TON' | '0 TON' | '0.000309 TON' | 0 |
| 8 | '0x0' | '1.088638 TON' | '0 TON' | '0.000309 TON' | 0 |
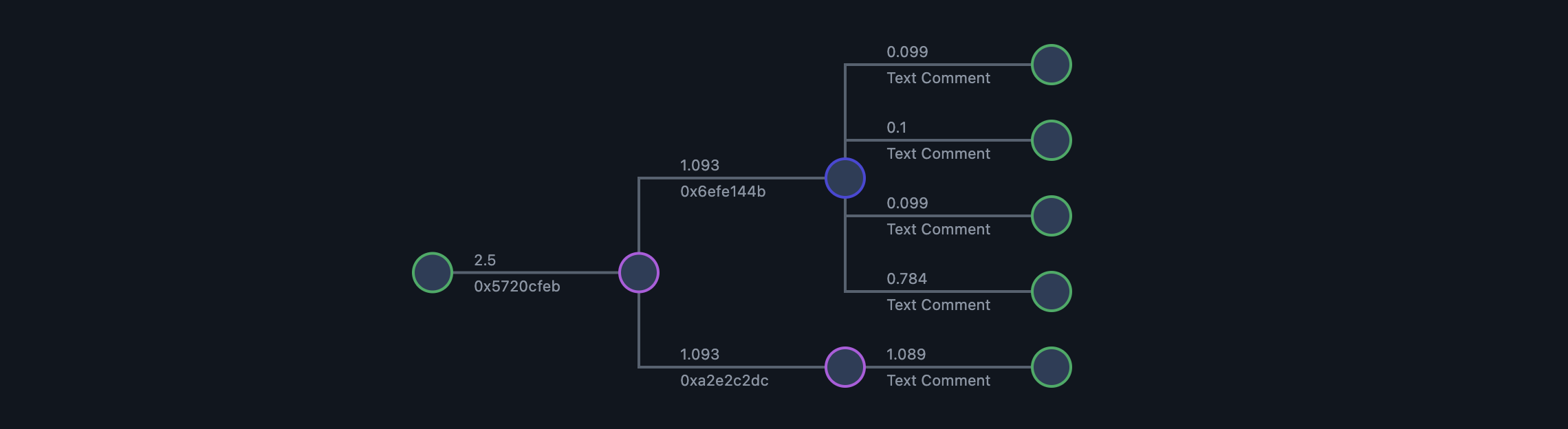
index - 是launchResult数组中交易的ID。
0- 对资金库(the Launcher)的外部请求,导致发送消息op::set_first到Fireworks1- 导致发送4条消息到the Launcher的Fireworks交易2- 在Launched Fireworks - 1中从the Launcher收到消息,消息使用op::launch_first操作码发送。2- 在Launched Fireworks - 2中从the Launcher收到消息,消息使用op::launch_second操作码发送。4- 在the Launcher中收到来自Launched Fireworks - 1的消息的交易,消息以send mode = 0发送5- 在the Launcher中收到来自Launched Fireworks - 1的消息的交易,消息以send mode = 1发送6- 在the Launcher中收到来自Launched Fireworks - 1的消息的交易,消息以send mode = 2发送7- 在the Launcher中收到来自Launched Fireworks - 1的消息的交易,消息以send mode = 128 + 32发送8- 在the Launcher中收到来自Launched Fireworks - 2的消息的交易,消息以send mode = 64发送
交易费用测试
此测试验证启动fireworks的交易费用是否符合预期。可以为佣金费用的不同部分进行自定义定价。
it('should be executed with expected fees', async() => {
const launcher = await blockchain.treasury('launcher');
const launchResult = await fireworks.sendDeployLaunch(
launcher.getSender(),
toNano('2.5'),
);
//totalFee
console.log('total fees = ', launchResult.transactions[1].totalFees);
const tx1 = launchResult.transactions[1];
if (tx1.description.type !== 'generic') {
throw new Error('Generic transaction expected');
}
//computeFee
const computeFee = tx1.description.computePhase.type === 'vm' ? tx1.description.computePhase.gasFees : undefined;
console.log('computeFee = ', computeFee);
//actionFee
const actionFee = tx1.description.actionPhase?.totalActionFees;
console.log('actionFee = ', actionFee);
if ((computeFee == null || undefined) ||
(actionFee == null || undefined)) {
throw new Error('undefined fees');
}
//The check, if Compute Phase and Action Phase fees exceed 1 TON
expect(computeFee + actionFee).toBeLessThan(toNano('1'));
});
极端情况测试
在本节中,将提供在交易处理期间可能发生的TVM exit codes(退出代码)的测试用例。这些exit codes在区块链代码本身中。同时,必须区分在Compute Phase( Compute Phase )和Action Phase(行动阶段)期间的exit code。
Compute Phase期间执行合约逻辑(其代码)。在处理期间,可以创建不同的action(动作)。这些action将在下一阶段 - Action Phase处理。如果Compute Phase不成功,则Action Phase不开始。然而,如果Compute Phase成功,这并不保证Action Phase也会成功结束。
Compute Phase | exit code = 0
此exit code表示交易的Compute Phase已成功完成。
Compute Phase | exit code = 1
标记Compute Phase成功的另一种exit code是1。要获得此exit code,您需要使用RETALT。
值得注意的是,这个操作码应该在主函数中调用(例如,recv_internal)。如果在另一个函数中调用,则该函数的exit将为1,但总体exit code将为0。
Compute Phase | exit code = 2
TVM是堆栈机。与不同值交互时,它们会出现在堆栈上。如果突然堆栈上没有元素,但某些操作码需要它们,那么将抛出此错误。
这可能发生在直接使用操作码时,因为stdlib.fc(FunC的库)假设不会有这样的问题。
Compute Phase | exit code = 3
任何代码在执行前都变成了continuation。这是一种特殊的数据类型,包含有代码的切片、堆栈、寄存器和其他执行代码所需的数据。如果需要,这种continuation可以在稍后运行,来传递开始执行堆栈的必要参数。
首先,我们构建这样的continuation。在这种情况下,这只是一个空的continuation,什么也不做。接下来,使用操作码0 SETNUMARGS,我们指示在执行开始时堆栈中不应有值。然后,使用操作码1 -1 SETCONTARGS,我们调用continuation,传递1个值。由于本来应该没有值,因此我们得到了StackOverflow错误。
Compute Phase | exit code = 4
在TVM中,integer可以在-2256 \< x \< 2256范围内。如果在计算过程中值超出此范围,则抛出exit code 4。
Compute Phase | exit code = 5
如果integer值超出预期范围,则抛出exit code 5。例如,如果在.store_uint()函数中使用了负值。
Compute Phase | exit code = 6
在较低层级,使用操作码而不是熟悉的函数名称,可以在此表中以HEX形式看到。在这个例子中,我们使用@addop,添加了一个不存在的操作码。
模拟器在尝试处理此操作码时无法识别它,并抛出 6。
Compute Phase | exit code = 7
这是一个发生在接收到错误的数据类型时的很常见的错误。在示例中,tuple包含3个元素,但在解包时尝试获取4个。
还有许多其他情况会抛出此错误。其中一些:
- not a null
- not an integer
- not a cell
- not a cell builder
- not a cell slice
- not a string
- not a bytes chunk
- not a continuation
- not a box
- not a tuple
- not an atom
Compute Phase | exit code = 8
TON 中的所有数据都存储在 cells 中。一个单元格可存储 1023 位数据和 4 个指向其他单元格的引用。如果尝试写入超过 1023 位的数据或超过 4 个引用,将抛出 exit code 8。
Compute Phase | exit code = 9
如果尝试从切片中读取比它包含的更多数据(从cell中读取数据时,必须将其转换为切片数据类型),则抛出exit code 9。例如,如果切片中有10位,而读取了11位,或者如果没有对其他引用的链接,但尝试加载引用。
Compute Phase | exit code = 10
此错误在处理字典时抛出。例如,当值属于键时存储在另一个cell中作为引用。在这种情况下,您需要使用.udict_get_ref()函数来获取这样的值。
然而,另一个cell中的链接应该只有1个,而不是2个,如我们的例子:
root_cell
├── key
│ ├── value
│ └── value - second reference for one key
└── key
└── value
这就是为什么在尝试读取数值时,我们会得到 exit code 10。
附加: 您还可以在字典中存储键旁的值:
root_cell
├── key-value
└── key-value
注意: 实际上,字典的结构(数据如何放置在cell中)比上面的示例更复杂。因此,它们被简化了,以便理解示例。
Compute Phase | exit code = 11
此错误发生在未知情况。例如,在使用SENDMSG操作码时,如果传递了错误(例如,空的)的消息cell,那么就会发生这种错误。
此外,它还在尝试调用不存在的方法时发生。开发人员通常是在调用不存在的GET方法时面临这种情况。
Compute Phase | exit code = -14 (13)
如果处理Compute Phase的TON不足,则抛出此错误。在枚举类Excno中,其中指示了Compute Phase中各种错误的exit code,指示的值为13。
然而,在处理过程中,对此值应用了NOT操作,将此值更改为-14。这样做是为了这个exit code不能被伪造,例如使用throw函数,因为所有这些函数只接受exit code是正值。
Action Phase | exit code = 32
Action Phase在Compute Phase之后开始,它处理在Compute Phase期间写入寄存器c5的动作。如果此寄存器中的数据写入不正确,则抛出exit code 32。
Action Phase | exit code = 33
目前,一个交易中最多可以有255个动作。如果超过这个值,则Action Phase将以exit code 33 结束。
Action Phase | exit code = 34
Exit code是造成处理action时的大部分错误的原因:无效消息、不正确动作等。
Action Phase | exit code = 35
在构建消息的 CommonMsgInfo 部分时,必须指定正确的源地址。它必须等于addr_none 或发送消息的账户地址。
在区块链代码中,这由check_replace_src_addr处理。
Action Phase | exit code = 36
如果目的地地址无效,则抛出exit code 36。一些可能的原因是不存在的工作链或不正确的地址。所有检查都可以在check_rewrite_dest_addr中看到。
Action Phase | exit code = 37
此exit code类似于Compute Phase的-14。在这里,它意味着余额不足以发送指定金额的TON。
Action Phase | exit code = 38
与exit code 37相同,但指的是余额中缺乏ExtraCurrency。
Action Phase | exit code = 40
在这种情况下,有足够的TON来处理消息的某个部分(比如说5个cell),而消息中有10个cell,将抛出exit code 40。
Action Phase | exit code = 43
可能发生的情况是超过了库中cell的最大数量或超过了Merkle树的最大深度。
库是存储在Masterchain中的cell,如果它是公开的,可以被所有智能合约使用。
由于更新代码时行的顺序可能会改变,一些链接变得不相关。因此,所有链接都将使用提交9728bc65b75defe4f9dcaaea0f62a22f198abe96时的代码库状态。








